MELSEC Tutorial 13 – Debugging and Maintenance
Efficient debugging and maintenance are critical aspects of working with MELSEC PLC systems, ensuring smooth operation and quick troubleshooting. This tutorial covers how to use GX Works3 to debug programs, monitor PLC performance, and carry out essential maintenance tasks.

-
MELSEC Tutorial 01 – PLC System Configuration

MELSEC Tutorial 01 – System Configuration, Installation, and Wiring Setting up a MELSEC PLC system is the first step in…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 02 – PLC Module Configuration Diagram

MELSEC Tutorial 02 – Module Configuration Diagram Creating a module configuration diagram is a critical step in setting up a…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 03 – Ladder Program
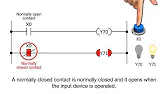
MELSEC Tutorial 03 – Ladder Program In industrial automation, programming controls the behavior of devices and systems. MELSEC Ladder Programming…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 04 – Create a Ladder Program
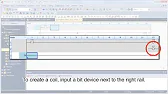
MELSEC Tutorial 04 – Create a Ladder Program Industrial automation relies heavily on programming to implement control logic for machines…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 05 – Ladder Sequence Instructions
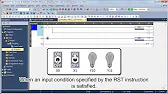
MELSEC Tutorial 05 – Ladder Logic Programming Sequence Instructions Ladder Logic Programming is a vital skill for developing control systems…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 06 – Ladders Timers and Counters
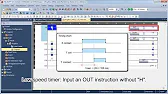
MELSEC Tutorial 06 – Ladder Logic Programming: Timer and Counter MELSEC Timers and counters are fundamental tools in ladder logic…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 07 – Ladder Logic Programming Data Transfer
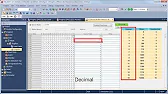
MELSEC Tutorial 07 – Ladder Logic Programming: Data Transfer In ladder logic programming, data transfer instructions are crucial for moving…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 08 – Ladder Comparison Operations
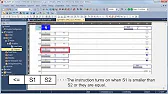
MELSEC Tutorial 08 – Ladder Logic Programming: Comparison Operation In industrial automation, MELSEC comparison operations play a vital role in…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 09 – Ladder Arithmetic Operations

MELSEC Tutorial 09 – Ladder Logic Programming: Arithmetic Operations MELSEC arithmetic operations form the backbone of ladder logic programming, enabling…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 10 – Ladder Input Instructions
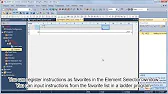
MELSEC Tutorial 10 – Ladder Logic Programming: Input Instructions MELSEC Ladder logic programming depends on input instructions to define how…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 11 – Creating ladder logic comments
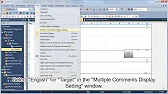
MELSEC ladder logic Creating Comments, Statements, and Notes When programming with ladder logic, clarity is essential to ensure the program…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 12 – Writing to PLC
MELSEC Tutorial 12 – Writing to PLC In this tutorial, we’ll explore how to write programs to a PLC using…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 13 – Debugging and Maintenance

MELSEC Tutorial 13 – Debugging and Maintenance Efficient debugging and maintenance are critical aspects of working with MELSEC PLC systems,…
Debugging with GX Works3
Step 1: Using the Online Monitor
- Connect to the PLC: Establish communication between GX Works3 and the PLC as explained in previous tutorials.
- Activate Online Mode: In GX Works3, go to the Online menu and select Monitor Mode.
- Monitor Device Values:
- Use the Watch Window to observe real-time values of devices like timers, counters, and data registers.
- Modify values directly if needed for testing purposes.
Step 2: Using Forced Operations
Forcing devices allows you to simulate input/output conditions:
- Right-click on the target device in the Watch Window.
- Select Force On or Force Off to control the device manually.
- Observe the program’s response and verify that the logic behaves as intended.
Step 3: Diagnosing Errors
- Access the Error History from the Diagnostics menu.
- Review detailed error messages, including timestamps and affected modules.
- Resolve issues based on suggested solutions, such as correcting mismatched parameters or clearing overloaded registers.
Maintenance Procedures
1: Regular Backup
- Use the Read from PLC function to retrieve the current program and device settings from the PLC.
- Save the backup project file to a secure location for future restoration.
2: System Performance Checks
- Access the Device Memory Monitor to check the usage and health of memory areas.
- Evaluate CPU load and cycle times to ensure optimal performance.
3: Firmware Updates
- Periodically check for firmware updates for your MELSEC PLC modules.
- Use GX Works3 or Mitsubishi’s dedicated tools to apply updates while minimizing downtime.
Common Debugging and Maintenance Issues
- Communication Failures: Ensure correct connection settings and verify physical cabling.
- Logic Errors: Use step-by-step execution or simulation mode to identify and fix programming issues.
- Module Malfunctions: Inspect and replace faulty hardware components as necessary.
Best Practices for Debugging and Maintenance
- Use Simulation Mode: Debug programs in simulation before deploying them to live PLCs.
- Document Changes: Maintain detailed logs of program modifications and maintenance activities.
- Schedule Preventative Maintenance: Regularly check hardware and software to prevent unexpected failures.
Conclusion

Debugging and maintaining MELSEC PLC systems are vital for ensuring reliable operation and optimizing performance. By leveraging GX Works3’s powerful diagnostic tools and adhering to best practices, you can resolve issues quickly and maintain your systems efficiently.
