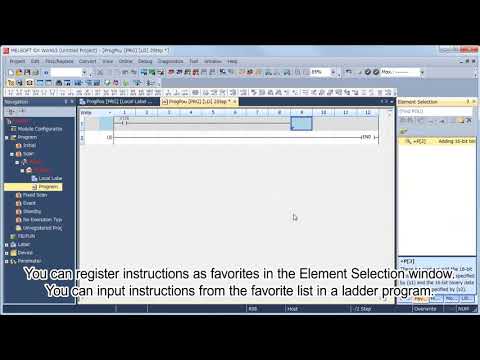
MELSEC Tutorial 10 – Ladder Logic Programming: Input Instructions
MELSEC Ladder logic programming depends on input instructions to define how a PLC interprets signals from external devices. These instructions form the foundation for controlling processes in industrial automation. In this tutorial, we will explore in MELSEC how to input instructions effectively in GX Works3, focusing on key instruction types such as contacts and coils.
-
MELSEC Tutorial 01 – PLC System Configuration

MELSEC Tutorial 01 – System Configuration, Installation, and Wiring Setting up a MELSEC PLC system is the first step in…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 02 – PLC Module Configuration Diagram

MELSEC Tutorial 02 – Module Configuration Diagram Creating a module configuration diagram is a critical step in setting up a…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 03 – Ladder Program
MELSEC Tutorial 03 – Ladder Program In industrial automation, programming controls the behavior of devices and systems. MELSEC Ladder Programming…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 04 – Create a Ladder Program
MELSEC Tutorial 04 – Create a Ladder Program Industrial automation relies heavily on programming to implement control logic for machines…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 05 – Ladder Sequence Instructions
MELSEC Tutorial 05 – Ladder Logic Programming Sequence Instructions Ladder Logic Programming is a vital skill for developing control systems…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 06 – Ladders Timers and Counters
MELSEC Tutorial 06 – Ladder Logic Programming: Timer and Counter MELSEC Timers and counters are fundamental tools in ladder logic…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 07 – Ladder Logic Programming Data Transfer
MELSEC Tutorial 07 – Ladder Logic Programming: Data Transfer In ladder logic programming, data transfer instructions are crucial for moving…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 08 – Ladder Comparison Operations
MELSEC Tutorial 08 – Ladder Logic Programming: Comparison Operation In industrial automation, MELSEC comparison operations play a vital role in…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 09 – Ladder Arithmetic Operations

MELSEC Tutorial 09 – Ladder Logic Programming: Arithmetic Operations MELSEC arithmetic operations form the backbone of ladder logic programming, enabling…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 10 – Ladder Input Instructions
MELSEC Tutorial 10 – Ladder Logic Programming: Input Instructions MELSEC Ladder logic programming depends on input instructions to define how…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 11 – Creating ladder logic comments
MELSEC ladder logic Creating Comments, Statements, and Notes When programming with ladder logic, clarity is essential to ensure the program…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 12 – Writing to PLC
MELSEC Tutorial 12 – Writing to PLC In this tutorial, we’ll explore how to write programs to a PLC using…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 13 – Debugging and Maintenance

MELSEC Tutorial 13 – Debugging and Maintenance Efficient debugging and maintenance are critical aspects of working with MELSEC PLC systems,…
Understanding Input Instructions in Ladder Logic
Input instructions enable a PLC to monitor and respond to signals from field devices like sensors, switches, and buttons. The most common input instructions include:
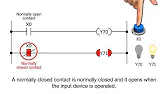
- Normally Open (NO) Contact: Activates when the input signal is ON.
- Normally Closed (NC) Contact: Activates when the input signal is OFF.
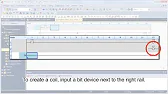
- Coil Instruction: Controls outputs based on input logic.
Step 1: Setting Up Input Devices
Connecting Field Devices
Ensure your input devices (e.g., push buttons, limit switches) are properly wired to the PLC’s input terminals. Use the system’s input wiring diagram to connect each device to its designated terminal.
Assigning Device Addresses
Assign appropriate device addresses (e.g., X0, X1) for the input terminals. These addresses correspond to the input signals in ladder logic.
Step 2: Inputting Basic Instructions
Example 1: Using a Normally Open Contact
Scenario: Activate a motor (Y0) when a start button (X0) is pressed.
- Open the ladder logic editor in GX Works3.
- Insert a Normally Open (NO) Contact instruction for
X0. - Add a coil instruction for
Y0, connecting it toX0.
Ladder Logic Code:
--[ X0 ]--------------------( Y0 )--
When X0 (start button) is ON, the motor (Y0) turns ON.
Example 2: Using a Normally Closed Contact
Scenario: Stop the motor (Y0) when a stop button (X1) is pressed.
- Add a Normally Closed (NC) Contact instruction for
X1. - Place the NC contact in series with the NO contact from Example 1.
Ladder Logic Code:
--[ X0 ]---|/| X1 ---------( Y0 )--
When X1 (stop button) is pressed, Y0 turns OFF.
Example 3: Using Multiple Inputs
Scenario: Activate a conveyor belt (Y1) when both sensors (X2 and X3) detect items.
- Insert two NO contact instructions for
X2andX3. - Connect the contacts in series to a coil instruction for
Y1.
Ladder Logic Code:
--[ X2 ]---[ X3 ]---------( Y1 )--
The conveyor belt activates only when both X2 and X3 are ON.
Step 3: Advanced Input Techniques
Example: Parallel Inputs for OR Logic
Scenario: Start a pump (Y2) when either of two buttons (X4 or X5) is pressed.
- Add two NO contact instructions for
X4andX5. - Connect the contacts in parallel to a coil instruction for
Y2.
Ladder Logic Code:
--[ X4 ]--| |--[ X5 ]----( Y2 )--
The pump starts when either button is pressed.
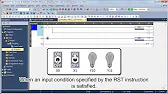
Latching an Output
Scenario: Keep a light (Y3) ON even after the button (X6) is released.
- Insert an NO contact instruction for
X6. - Add a coil instruction for
Y3. - Create a feedback loop by inserting a parallel NO contact linked to
Y3.
Ladder Logic Code:
--[ X6 ]--------------------( Y3 )--
| |
--[ Y3 ]------------------
The light remains ON until manually turned OFF.
Step 4: Testing and Debugging
Use the Simulation Mode in GX Works3 to test your ladder logic program. Monitor input statuses and verify the output behavior in real-time to ensure all instructions work as intended.
Conclusion

MELSEC Input instructions are essential for ladder logic programming, enabling the PLC to respond to external signals and execute processes effectively. By mastering the use of NO and NC contacts, coils, and advanced input configurations, you can create robust automation programs tailored to your needs.
