MELSEC Tutorial 08 – Ladder Logic Programming: Comparison Operation
In industrial automation, MELSEC comparison operations play a vital role in decision-making processes within ladder logic programming. These operations enable your MELSEC PLC to evaluate conditions and execute specific actions based on the results. This tutorial focuses on using comparison instructions like >, <, =, and others in GX Works3, guiding you through their implementation, application, and testing.
-
MELSEC Tutorial 01 – PLC System Configuration

MELSEC Tutorial 01 – System Configuration, Installation, and Wiring Setting up a MELSEC PLC system is the first step in…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 02 – PLC Module Configuration Diagram

MELSEC Tutorial 02 – Module Configuration Diagram Creating a module configuration diagram is a critical step in setting up a…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 03 – Ladder Program
MELSEC Tutorial 03 – Ladder Program In industrial automation, programming controls the behavior of devices and systems. MELSEC Ladder Programming…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 04 – Create a Ladder Program
MELSEC Tutorial 04 – Create a Ladder Program Industrial automation relies heavily on programming to implement control logic for machines…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 05 – Ladder Sequence Instructions
MELSEC Tutorial 05 – Ladder Logic Programming Sequence Instructions Ladder Logic Programming is a vital skill for developing control systems…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 06 – Ladders Timers and Counters
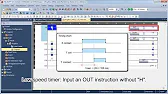
MELSEC Tutorial 06 – Ladder Logic Programming: Timer and Counter MELSEC Timers and counters are fundamental tools in ladder logic…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 07 – Ladder Logic Programming Data Transfer
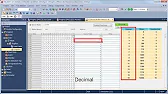
MELSEC Tutorial 07 – Ladder Logic Programming: Data Transfer In ladder logic programming, data transfer instructions are crucial for moving…
-
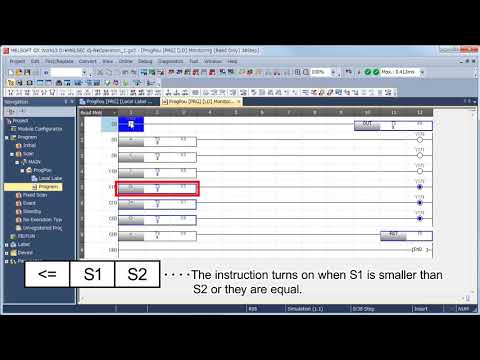
MELSEC Tutorial 08 – Ladder Comparison Operations
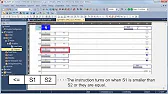
MELSEC Tutorial 08 – Ladder Logic Programming: Comparison Operation In industrial automation, MELSEC comparison operations play a vital role in…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 09 – Ladder Arithmetic Operations

MELSEC Tutorial 09 – Ladder Logic Programming: Arithmetic Operations MELSEC arithmetic operations form the backbone of ladder logic programming, enabling…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 10 – Ladder Input Instructions
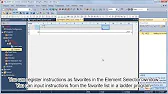
MELSEC Tutorial 10 – Ladder Logic Programming: Input Instructions MELSEC Ladder logic programming depends on input instructions to define how…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 11 – Creating ladder logic comments
MELSEC ladder logic Creating Comments, Statements, and Notes When programming with ladder logic, clarity is essential to ensure the program…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 12 – Writing to PLC
MELSEC Tutorial 12 – Writing to PLC In this tutorial, we’ll explore how to write programs to a PLC using…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 13 – Debugging and Maintenance

MELSEC Tutorial 13 – Debugging and Maintenance Efficient debugging and maintenance are critical aspects of working with MELSEC PLC systems,…
What Are MELSEC Comparison Operations?
MELSEC comparison operations compare two values, such as constants, data registers, or variables. Based on the result, they trigger specific outputs or actions in the ladder logic program. Common comparison operators include:
>: Greater than<: Less than=: Equal to>=: Greater than or equal to<=: Less than or equal to!=: Not equal to
Step 1: Setting Up Registers and Inputs
Before programming, prepare your GX Works3 project:
- Open your project and access the Device/Label Editor.
- Define data registers for comparison. For example:
- Register
D0: Input Value - Register
D1: Threshold Value
- Register
- Assign test values to these registers for simulation.
Step 2: Implementing Basic Comparison
Example: Greater Than (>)
Scenario: Activate an output if the value in D0 is greater than 100.
- Insert a comparison instruction:
- Use
>to compareD0with the constant100.
- Use
- Link the comparison to a coil (output).
Ladder Logic Code:
D0 > K100 --] [-- Output --( )--
When D0 exceeds 100, the output coil activates.
Step 3: Using Multiple Conditions
Example: Between (>= and <=)
Scenario: Trigger an output if the value in D0 lies between 50 and 150.
- Create two conditions:
D0 >= K50D0 <= K150
- Use an AND block to combine the conditions.
Ladder Logic Code:
D0 >= K50 --] [--+--] [-- D0 <= K150 --( )--
The output activates when both conditions are true.
Step 4: Comparison with Data Registers
Example: Not Equal (!=)
Scenario: Activate a warning if D0 and D1 contain different values.
- Insert a
!=instruction to compareD0withD1. - Link the result to a warning indicator coil.
Ladder Logic Code:
D0 != D1 --] [-- Warning --( )--
Step 5: Real-Time Monitoring
To verify comparison operations:
- Open the Device/Monitor tool in GX Works3.
- Add the registers (
D0,D1, etc.) to the watchlist. - Modify register values during simulation and observe how the program responds to changes.
Step 6: Advanced Application
Example: Greater Than and Output Assignment
Scenario: If D0 > D1, transfer D0 to D2.
- Use a comparison instruction (
>). - Link it to a MOV instruction to move the value of
D0toD2.
Ladder Logic Code:
D0 > D1 --] [-- MOV D0 D2 --( )--
When the condition is met, the program automatically transfers data.
Step 7: Combining Comparisons with Timers
Combine comparison operations with timer functions for enhanced functionality.
Scenario: Turn on an alarm if D0 < 50 for more than 5 seconds.
- Insert a
<instruction to compareD0and50. - Link the comparison result to a TON (Timer On-Delay).
- Connect the timer’s output to an alarm coil.
Ladder Logic Code:
D0 < K50 --] [-- TON T0 K500 --] [-- Alarm --( )--
Conclusion

MELSEC comparison operations are an essential part of ladder logic programming, enabling dynamic control and decision-making. Mastering these operations in GX Works3 allows you to build smarter, more responsive automation systems with your MELSEC PLC.
