MELSEC Tutorial 04 – Create a Ladder Program
Industrial automation relies heavily on programming to implement control logic for machines and processes. Ladder Programming, the graphical representation of logic circuits, is widely used for configuring Mitsubishi Electric’s MELSEC PLCs. In this tutorial, we’ll cover the step-by-step process how to create a MELSEC ladder program. You’ll learn how to design and implement logic structures, incorporate advanced functions, and test your program effectively.

-
MELSEC Tutorial 01 – PLC System Configuration

MELSEC Tutorial 01 – System Configuration, Installation, and Wiring Setting up a MELSEC PLC system is the first step in…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 02 – PLC Module Configuration Diagram

MELSEC Tutorial 02 – Module Configuration Diagram Creating a module configuration diagram is a critical step in setting up a…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 03 – Ladder Program
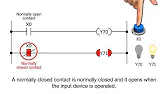
MELSEC Tutorial 03 – Ladder Program In industrial automation, programming controls the behavior of devices and systems. MELSEC Ladder Programming…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 04 – Create a Ladder Program
MELSEC Tutorial 04 – Create a Ladder Program Industrial automation relies heavily on programming to implement control logic for machines…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 05 – Ladder Sequence Instructions
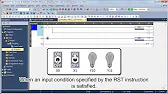
MELSEC Tutorial 05 – Ladder Logic Programming Sequence Instructions Ladder Logic Programming is a vital skill for developing control systems…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 06 – Ladders Timers and Counters
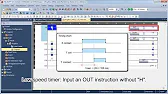
MELSEC Tutorial 06 – Ladder Logic Programming: Timer and Counter MELSEC Timers and counters are fundamental tools in ladder logic…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 07 – Ladder Logic Programming Data Transfer
MELSEC Tutorial 07 – Ladder Logic Programming: Data Transfer In ladder logic programming, data transfer instructions are crucial for moving…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 08 – Ladder Comparison Operations
MELSEC Tutorial 08 – Ladder Logic Programming: Comparison Operation In industrial automation, MELSEC comparison operations play a vital role in…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 09 – Ladder Arithmetic Operations

MELSEC Tutorial 09 – Ladder Logic Programming: Arithmetic Operations MELSEC arithmetic operations form the backbone of ladder logic programming, enabling…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 10 – Ladder Input Instructions
MELSEC Tutorial 10 – Ladder Logic Programming: Input Instructions MELSEC Ladder logic programming depends on input instructions to define how…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 11 – Creating ladder logic comments
MELSEC ladder logic Creating Comments, Statements, and Notes When programming with ladder logic, clarity is essential to ensure the program…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 12 – Writing to PLC
MELSEC Tutorial 12 – Writing to PLC In this tutorial, we’ll explore how to write programs to a PLC using…
-
MELSEC Tutorial 13 – Debugging and Maintenance

MELSEC Tutorial 13 – Debugging and Maintenance Efficient debugging and maintenance are critical aspects of working with MELSEC PLC systems,…
What is Ladder Programming?
Ladder Logic mimics electrical relay circuits using graphical elements like contacts, coils, and rungs. Each rung represents a logical condition or operation, enabling simple and effective programming of industrial systems. It is especially popular for programming PLCs due to its intuitive design.
Step 1: Setting Up MELSOFT GX Works3
Before starting your ladder program, ensure you have the necessary software and hardware setup.
Prerequisites:
- MELSEC PLC hardware: A configured and connected PLC.
- MELSOFT GX Works3: Mitsubishi’s programming software.
- Connection Cable: USB, Ethernet, or RS232, depending on your PLC model.
Installing the Software:
- Download and install GX Works3 from the Mitsubishi Electric website.
- Launch the software and connect your MELSEC PLC.
- Create a new project and select your PLC model (e.g., iQ-F or iQ-R series).
Step 2: Understanding Ladder Diagram Components
Basic Elements:
- Contacts: Represent input conditions (e.g., a sensor or switch).
- Coils: Represent output actions (e.g., a motor or alarm).
- Timers and Counters: Used for time-based and count-based logic.
Logical Structures:
- AND Logic: Two or more contacts in series.
- OR Logic: Two or more contacts in parallel.
- Latch Circuits: Maintain the state of an output until explicitly reset.
Step 3: Create the MELSEC ladder program
Start with the Input and Output Definitions:
- Open the Ladder Editor in GX Works3.
- Define the input devices (e.g., start button, stop button) and assign them to input addresses.
- Define the output devices (e.g., motor, light) and assign them to output addresses.
Write the Ladder Logic:
Example: Motor Control Logic
Create a circuit to turn on a motor when a start button is pressed and turn it off with a stop button.
- Add a normally open contact for the start button.
- Add a normally closed contact for the stop button.
- Connect these to a coil representing the motor.
plaintextCopy code Start Button --] [-- Stop Button --]/[-- Motor Coil --( )--
Step 4: Adding Advanced Functions
Using Timers:
- Select a TON (On-delay Timer) from the function block library.
- Configure the timer with a specific delay (e.g., 5 seconds).
- Connect the timer to the input and output for time-dependent operations.
Timer Example:
- A conveyor belt starts after a 5-second delay when a sensor is activated.
plaintextCopy code Sensor --] [-- Timer (TON) -- Conveyor --( )--
Using Counters:
- Add a Counter Block (CTU) to count events like part detection.
- Configure the counter with a preset value (e.g., count 10 parts before activating an output).
Step 5: Testing and Debugging the Ladder Program
Testing ensures your program works as intended.
- Simulate the Program:
- Use the GX Works3 simulator to test logic without connecting to hardware.
- Monitor the virtual inputs and outputs for proper functionality.
- Load the Program:
- Download the ladder logic to the PLC.
- Connect physical inputs (e.g., buttons, sensors) and verify that outputs (e.g., motors, alarms) respond correctly.
- Debug Errors:
- Use the debugging tools in GX Works3 to identify and fix issues.
- Check the wiring and input/output addresses if problems persist.
Conclusion

To create a ladder program for MELSEC PLCs involves understanding ladder logic, designing logical structures, and testing the program thoroughly. This tutorial covered basic and advanced ladder programming concepts, enabling you to implement logic for various automation tasks. Continue exploring more complex functions like subroutines and advanced data handling in future tutorials.
