Mitsubishi Inverters Quick Tips
Mitsubishi Electric inverters are renowned for their reliability, efficiency, and advanced control features in industrial automation. The Mitsubishi Inverters Quick Tips are designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of Mitsubishi inverters, covering essential aspects such as system setup, parameter configuration, and operation. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced professional, this guide will help you maximize the potential of these versatile devices.
-
Change Monitor Display for Mitsubishi D700 and E700 Inverters

Change Monitor Display for Mitsubishi D700 and E700 Inverters Mitsubishi Electric’s D700 and E700 inverter series are equipped with versatile…
-
Change Monitor Display for Mitsubishi FR PU07

Change Monitor Display for Mitsubishi FR PU07 Inverters Mitsubishi Electric’s FR PU07 inverter series are equipped with versatile monitoring and…
-
Clearing an E6 Warnings on a Mitsubishi Servo Amplifier
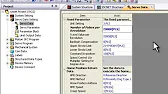
Guide to Clearing Mitsubishi Errors and Warnings Properly addressing errors and warnings on Mitsubishi devices like motion controllers, CPUs, and…
-
Clearing an E7 Warnings on a Mitsubishi Servo Amplifier

Guide to Clearing Mitsubishi Errors and Warnings Properly addressing errors and warnings on Mitsubishi devices like motion controllers, CPUs, and…
-
Clearing Multiple Mitsubishi CPU Errors

Guide to Clearing Mitsubishi Errors and Warnings Properly addressing errors and warnings on Mitsubishi devices like motion controllers, CPUs, and…
-
Clearing the AL L01 Motion Controller Mitsubishi Errors

Guide to Clearing Mitsubishi Errors and Warnings Properly addressing errors and warnings on Mitsubishi devices like motion controllers, CPUs, and…
-
Mitsubishi FR DU07 Parameter Download
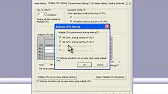
Mitsubishi FR PU07/FR DU07 Parameter Upload and Download Guide The Mitsubishi FR PU07 and FR DU07 parameter setting units are…
-
Mitsubishi FR DU07 Parameter Upload Download

Mitsubishi FR PU07/FR DU07 Parameter Upload and Download Guide The Mitsubishi FR PU07 and FR DU07 parameter setting units are…
-
Mitsubishi FR PU07 Connection to FR D700

Mitsubishi FR PU07/FR DU07 Parameter Upload and Download Guide The Mitsubishi FR PU07 and FR DU07 parameter setting units are…
-
Mitsubishi FR PU07 Connection to FR E700

Mitsubishi FR PU07/FR DU07 Parameter Upload and Download Guide The Mitsubishi FR PU07 and FR DU07 parameter setting units are…
-
Mitsubishi FR PU07 Parameter Upload

Mitsubishi FR PU07/FR DU07 Parameter Upload and Download Guide The Mitsubishi FR PU07 and FR DU07 parameter setting units are…
-
Mitsubishi PU07 Parameter Upload Download

Mitsubishi FR PU07/FR DU07 Parameter Upload and Download Guide The Mitsubishi FR PU07 and FR DU07 parameter setting units are…
-
Mitsubishi Quick Tips – Jogging a motor with the FR PU07
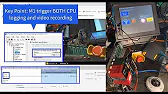
Mitsubishi Quick Tips – Jogging a motor with the FR PU07 Mitsubishi Electric’s Quick Tips series offers concise solutions to…
Understanding Mitsubishi Inverters Quick Tips
Mitsubishi inverters, also known as variable frequency drives (VFDs), control motor speed and torque by varying the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor. These inverters are widely used across industries for applications such as conveyor systems, HVAC systems, and machining operations.
Key Features of Mitsubishi Inverters
- Energy Efficiency: Optimized motor control reduces energy consumption.
- Versatility: Compatible with various motor types and industrial setups.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Built-in tools for monitoring and troubleshooting.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Simplified programming via control panels or software.
Training Modules
First Module: System Configuration and Installation
- Hardware Setup:
Mount the inverter securely in a well-ventilated area. Follow Mitsubishi’s guidelines for grounding and wiring connections. - Power Supply Connections:
Connect input and output power cables per the circuit diagram. Double-check voltage ratings to prevent damage.
Second Module: Parameter Configuration
- Accessing Parameters:
Use the keypad, HMI interface, or Mitsubishi’s FR Configurator2 software. - Key Parameters to Set:
- Motor Type and Rating: Input motor specifications like power, voltage, and frequency.
- Operation Mode: Set modes such as V/F control or vector control based on application needs.
- Acceleration and Deceleration Times: Adjust ramp-up and ramp-down times to ensure smooth operation.
Third Module: Operation Modes
- Manual Mode:
Operate the inverter directly using the control panel for testing or temporary control. - Automatic Mode:
Integrate with PLCs or external controllers for automated operations. - PID Control:
Use built-in PID settings for closed-loop control applications.
Fourth Module: Troubleshooting and Maintenance
- Common Faults:
Identify and resolve issues such as overvoltage, overcurrent, and overheating. - Preventive Maintenance:
Regularly inspect cooling fans, wiring connections, and filter systems to ensure long-term reliability.
Fifth Module: Advanced Features
- Networking and Communication:
Configure inverters for use with industrial communication protocols such as Modbus, EtherNet/IP, or CC-Link. - Energy Monitoring:
Leverage real-time monitoring tools to track power usage and optimize efficiency.
Practical Inverters Tips for Success

Update Firmware: Regularly check for firmware updates to access new features and fixes.
Understand Load Requirements: Ensure the inverter is correctly sized for the motor and application.
Use Safety Features: Activate protections like overload and short-circuit safeguards.
Keep Documentation Handy: Mitsubishi inverters come with comprehensive manuals—refer to them for detailed guidance.
