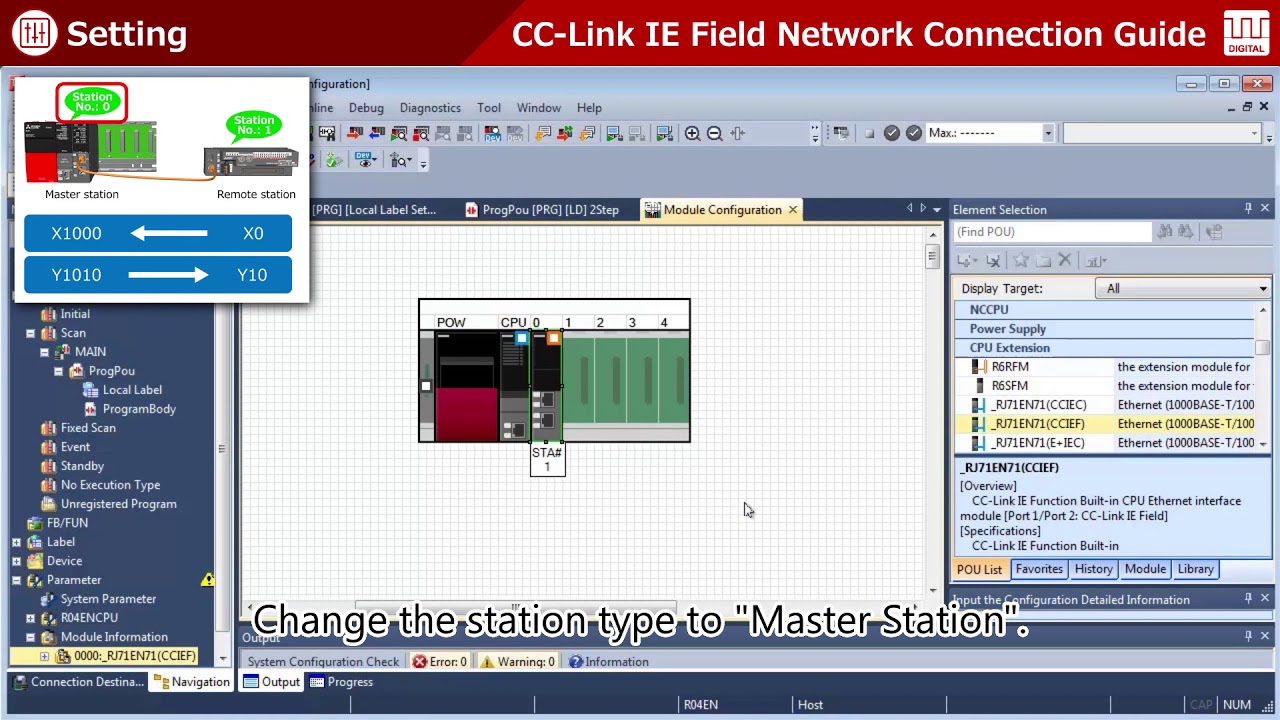
CC-Link IE Field Network Connection Guide – Digital I/O Software Settings
After configuring the hardware, setting up the software parameters for CC-Link IE Field Network Digital I/O is essential for proper communication and functionality. Software settings define how the digital I/O modules interact with the master station (PLC) and enable data exchange within the control system. This guide walks you through the steps to configure the necessary software settings. This guide is for digital I/O on a CC-Link IE Field Network, covering address mapping, parameter configuration, and testing.
-
Digital I/O 01 System configuration

CC-Link IE Field Network – System Configuration for Digital I/O Setting up the CC-Link IE Field Network for digital I/O…
-
Digital I/O 02 Hardware settings

CC-Link IE Field Network Connection Guide – Digital I/O Hardware Settings Setting up the hardware for CC-Link IE Field Network…
-
Digital I/O 03 Software settings
CC-Link IE Field Network Connection Guide – Digital I/O Software Settings After configuring the hardware, setting up the software parameters…
-
Digital I/O 04 Operation check

CC-Link IE Field Network Connection Guide – Digital I/O Operation Check Conducting a comprehensive operation check verifies that digital I/O…
Key Steps for Digital I/O Software Configuration on CC-Link IE Field Network
1. Defining the Network in Software
Using Mitsubishi’s GX Works3 (or relevant programming software), begin by creating a network project that includes your CC-Link IE Field Network.
- Create a New Project: Start by creating a new project for your CC-Link IE Field Network in GX Works3.
- Select Network Type: Choose “CC-Link IE Field Network” as the network type, ensuring the software is set up to communicate with the network.
- Add Modules: Add each digital I/O module to the network configuration in the software, representing each module on the actual network.
2. Configuring Station Numbers and Addresses
For each I/O module on the CC-Link IE Field Network, you’ll need to assign station numbers and device addresses in the software to match the physical hardware settings.
- Station Number Assignment: In the network configuration, assign station numbers that correspond to the physical switches or dip settings on each module.
- Address Mapping: Define the device addresses for each digital input and output point on the modules. The addresses should align with the PLC address map for accurate data exchange.
3. Setting I/O Parameters
With each module added to the project, configure the specific I/O parameters for your digital I/O devices. These settings tell the network how to interpret and handle each input and output signal.
- Input/Output Specifications: Set parameters that specify the type and function of each input and output (e.g., ON/OFF signals for digital inputs).
- Response Time: Configure response times if needed, which can determine how quickly the network reacts to changes in I/O signals. A faster response time may be crucial for time-sensitive operations.
4. Communication Settings for Network Stability
Ensuring reliable communication on the network is vital for smooth operations. Set up communication parameters for the CC-Link IE Field Network in your project.
- Transmission Speed: Select a transmission speed that matches the network hardware specifications (e.g., 1 Gbps).
- Error Detection and Handling: Enable error-detection protocols to identify and handle potential communication issues. This may include retries or fault-tolerance settings.
5. Downloading and Verifying Settings
Once all settings are configured, download the software configuration to the PLC to activate the network.
- Download Configuration: Send the network and I/O settings from GX Works3 to the master station (PLC) to apply the configuration.
- Verification: Check that the download was successful, and that all modules are recognized on the network.
6. Testing Digital I/O Functionality
After downloading the configuration, perform a test to ensure that each digital I/O module is correctly receiving and sending signals.
- Monitor I/O Points: Use the monitoring feature in GX Works3 to observe the status of each input and output point in real-time. Verify that inputs respond to connected devices (e.g., switches or sensors) and outputs activate the expected equipment.
- Simulation Mode: Run a simulation in GX Works3 to check for correct behavior of I/O functions without using live equipment. This allows for safer testing before full operation.
Best Practices for Software Configuration
- Label Each Device Address: Clearly label device addresses in the software to make it easy to identify each module’s function and I/O points.
- Match Software with Hardware: Ensure that all software configurations align with hardware settings, particularly for station numbers and addresses, to avoid communication errors.
- Save Regular Backups: Keep backups of your configuration in case adjustments or troubleshooting are needed in the future.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Device Not Recognized: If a device is not recognized on the network, double-check the station number in both the hardware and software settings.
- Incorrect Data Signals: Verify that address mappings are correct if you notice data discrepancies. Incorrect address assignments can lead to misinterpretations of input/output signals.
- Slow Response Times: Adjust the response time settings in the I/O parameters if you observe delays in signal transmission.
Conclusion

Properly setting up the software configuration for digital I/O on a CC-Link IE Field Network enables efficient communication between the PLC and digital devices, ensuring a seamless and responsive control system. By carefully defining station numbers, setting parameters, and verifying addresses. You can create a robust network setup that supports real-time operation and reliable data handling.
