CC-Link IE Field Network Basic Connection Guide – Operation Check
Once the CC-Link IE Field Network hardware and software configurations are complete, it’s crucial to perform an operation check to ensure everything is functioning as expected. This step verifies that communication between the master and slave devices is established correctly, and that all systems operate smoothly in real-world conditions.
This guide walks you through the process of conducting an operation check to confirm the correct setup of your CC-Link IE Field Network.
-
CC-Link IE Field Network Basic 01 Features – Operation

CC-Link IE Field Network Basic Connection Guide – Features and Operation The CC-Link IE Field Network is an industrial Ethernet-based…
-
CC-Link IE Field Network Basic 02 System Configuration
CC-Link IE Field Network Basic Connection Guide – System Configuration Establishing a reliable system configuration for the CC-Link IE Field…
-
CC-Link IE Field Network Basic 03 Hardware

CC-Link IE Field Network Basic Connection Guide – Hardware Setup Setting up the hardware configuration for the CC-Link IE Field…
-
CC-Link IE Field Network Basic 04 Software

CC-Link IE Field Network Basic Connection Guide – Software Configuration Configuring the software for your CC-Link IE Field Network is…
-
CC-Link IE Field Network Basic 05 Operation Check
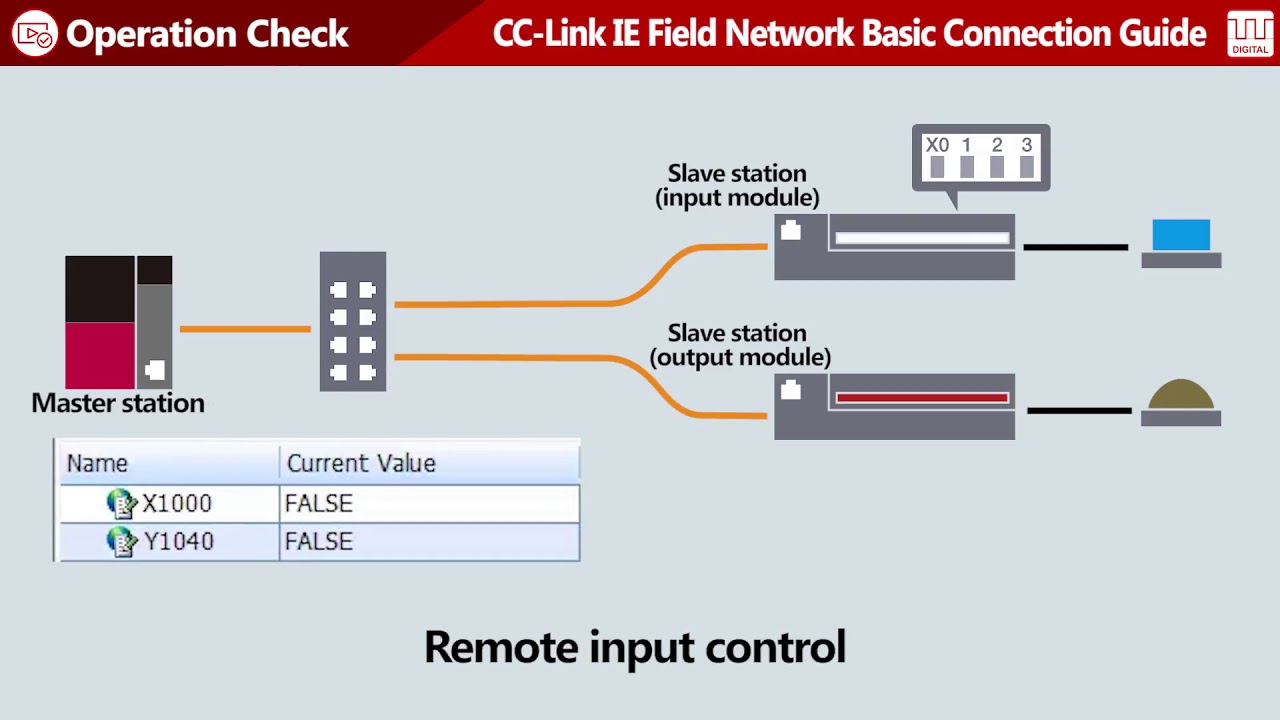
CC-Link IE Field Network Basic Connection Guide – Operation Check Once the CC-Link IE Field Network hardware and software configurations…
-
CC-Link IE Field Network Basic 06 Diagnostics

CC-Link IE Field Network Basic Connection Guide – Diagnostics After installing and configuring your CC-Link IE Field Network, it’s crucial…
1. Verifying Network Connection
Before performing a full operation check, the first step is to confirm that the network connections are functioning properly.
Steps for Verifying Network Connection:
- Connect Devices: Ensure all devices (PLC, I/O modules, sensors, etc.) are connected to the network properly, following the correct wiring and configuration.
- Check Device Status: On the master device (PLC), check the status of the CC-Link IE Field Network module. You should see an indicator showing that the devices are successfully connected.
- Use Monitoring Tools: In GX Works3, use network monitoring tools to verify that each device is online and can communicate with the PLC.
2. Running Initial Communication Tests
Once network connections are confirmed, run initial communication tests to validate data exchange between the master and slave devices.
Steps for Communication Testing:
- Activate Communication: On the master device, initiate the communication process between the PLC and the connected slave devices.
- Check Device Responses: Ensure that each slave device responds to communication requests from the master PLC. This includes verifying input and output signals, as well as any data exchange.
- Monitor Data Flow: Use GX Works3 to monitor real-time data flow between devices, checking for any delays, communication errors, or dropped signals.
3. Monitoring I/O Functionality
Next, verify that the digital and analog I/O devices are functioning correctly within the network.
Steps for Monitoring I/O Devices:
- Check Digital Inputs: Trigger digital inputs on the slave devices (e.g., turn on a sensor or button), and confirm that the master PLC receives the correct signals.
- Check Digital Outputs: Command the master PLC to activate digital outputs (e.g., turn on a motor or light) and check that the corresponding devices react as expected.
- Check Analog I/O: If using analog devices, test the analog inputs and outputs to ensure the system reads and writes values correctly, such as measuring temperature or pressure.
4. Test Data Transfer and Cycle Time
To ensure the CC-Link IE Field Network operates efficiently, test the speed and reliability of data transfer across the network, including communication cycle times.
Steps for Testing Data Transfer:
- Monitor Data Transfer Speed: In GX Works3, check the data transfer speed between devices. This is especially important for applications requiring real-time control.
- Verify Cycle Time: Ensure the communication cycle time is optimized for your application. Adjust the cycle time settings if necessary to avoid data delays.
- Check for Latency or Errors: Look for any latency or errors in data transfer. If detected, review device settings and network configuration to identify the cause of the issues.
5. Addressing Communication Errors
During the operation check, you may encounter communication issues. Here’s how to address them:
Steps for Resolving Errors:
- Review Error Codes: Use GX Works3 to review any error codes or warning messages that might appear during the operation check.
- Troubleshoot Connections: Check for loose or faulty connections, improper wiring, or incorrect network settings that could cause communication failures.
- Adjust Network Parameters: Modify network settings, such as IP addresses or cycle times, to resolve any communication problems.
- Re-test Devices: After making adjustments, re-test the devices to confirm that the issues have been resolved.
6. Final Check and System Validation
After addressing any errors and ensuring that all devices are communicating correctly, perform a final system check.
Final Steps:
- Run Full System Test: Perform a full system check to ensure that all devices work as expected, including I/O devices, sensors, and actuators.
- Confirm System Stability: Test the network under different operating conditions to ensure stability, ensuring the network can handle varying loads.
- Save and Document Settings: Once the operation check is complete, save the configuration settings in GX Works3 and document any changes made during the process.
Conclusion

An operation check is a crucial step in verifying that your CC-Link IE Field Network is working correctly after configuration. By running network, communication, I/O, and data transfer tests, you can ensure the stability and reliability of the system. Proper diagnostics and troubleshooting will help you address any issues and optimize the system for your specific application.
